Silicon Carbide Ceramic
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a ceramic material that ranks second only to diamond in hardness. It exhibits excellent heat dissipation, stable chemical properties, and a low surface friction coefficient. Consequently, its wear resistance is outstanding across various contact surfaces. Silicon carbide ceramics can maintain stability over a wide temperature range, minimizing thermal deformation and enabling their application in fields such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery.
Silicon Carbide Advantages
Hardness second only to diamond
SiC has extremely high temperature resistance
Excellent thermal conductivity
The thermal expansion coefficient of SiC is low (about 4.0 × 10 ⁻⁶/K)
Strong resistance to chemical corrosion
High fracture toughness and compressive strength
SiC material has good wear resistance
Excellent antioxidant properties
Can maintain high strength under both high and low temperature conditions
Low density, lighter than many metal materials
Silicon Carbide Uses
High temperature and high voltage power semiconductor devices
Mechanical wear-resistant seals
heat exchanger
Refractory lining
Gas turbine blades
SiC combustion nozzle
Optical reflector
High temperature sensor
SiC ceramic bearings
Power electronic heat dissipation substrate
High voltage transformer components
Products
-

 Silicon Carbide
Silicon Carbide -
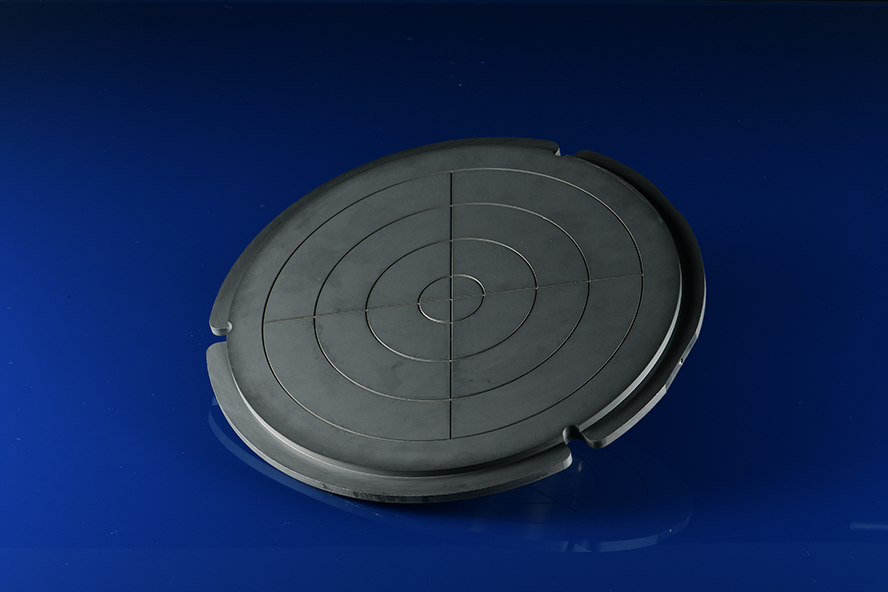


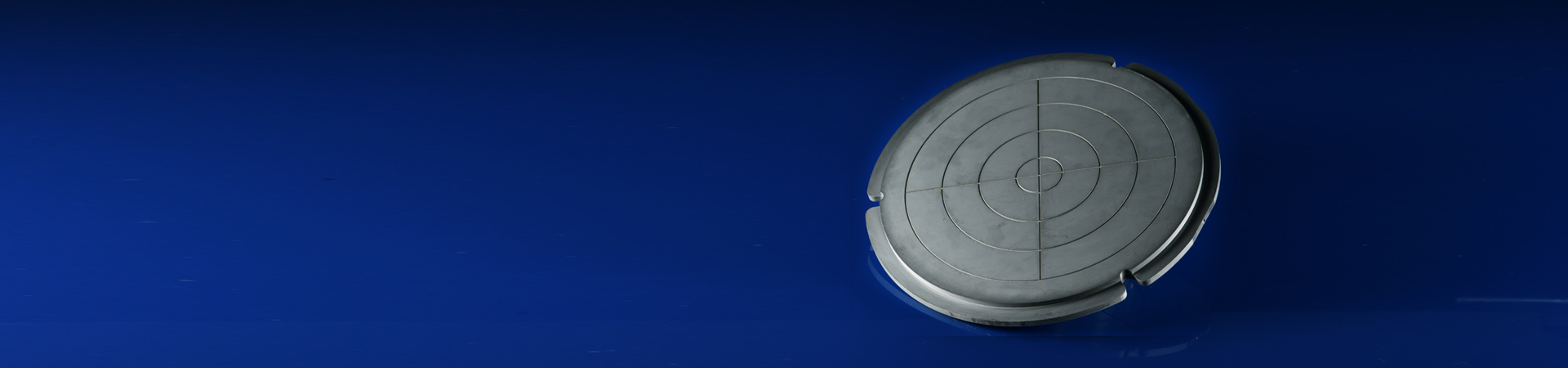
Silicon Carbide (SiC) Electrostatic Chuck
Silicon Carbide -
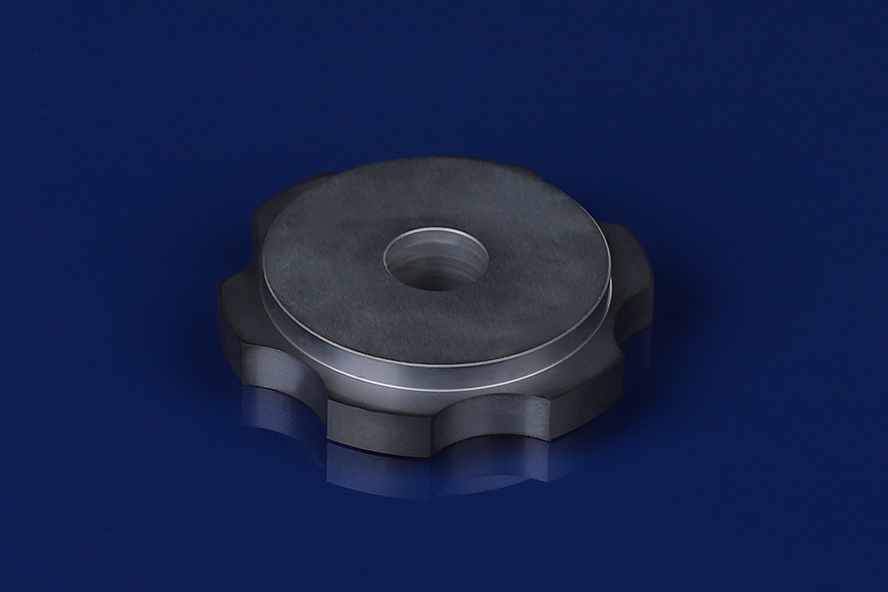
 Silicon Carbide
Silicon Carbide -

 Silicon Carbide
Silicon Carbide -
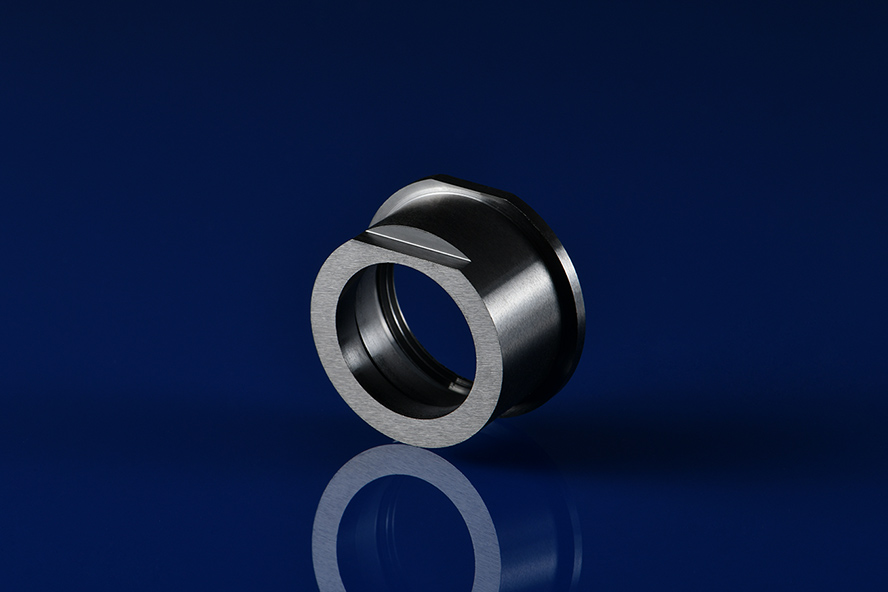


Silicon Carbide Ceramics Parts
Silicon Carbide -
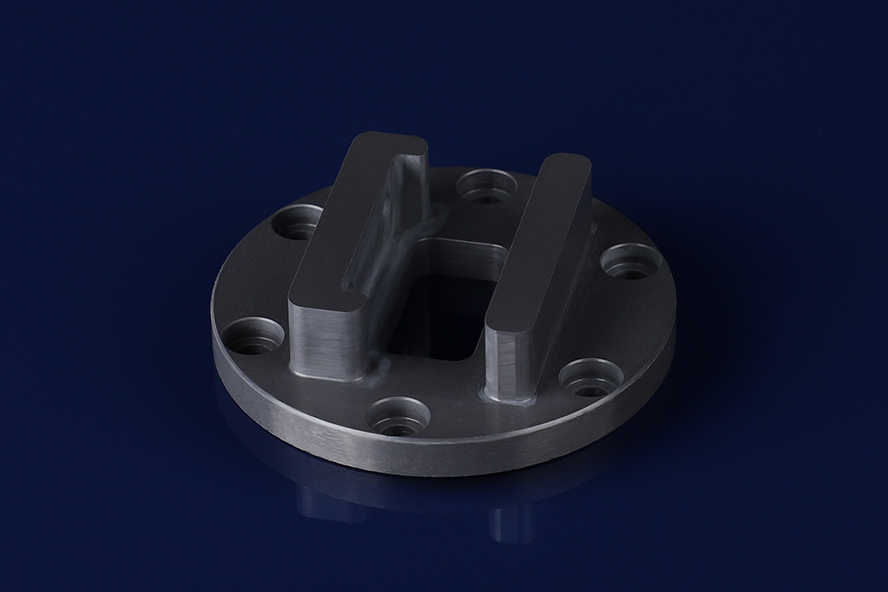


Silicon Carbide Ceramics Machining
Silicon Carbide -
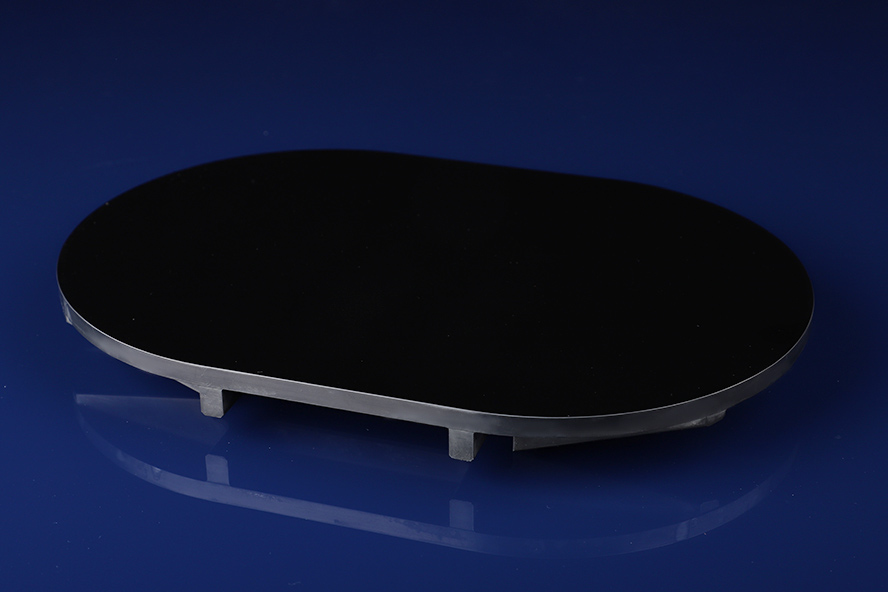


Silicon Carbide Optical Mirrors
Silicon Carbide -
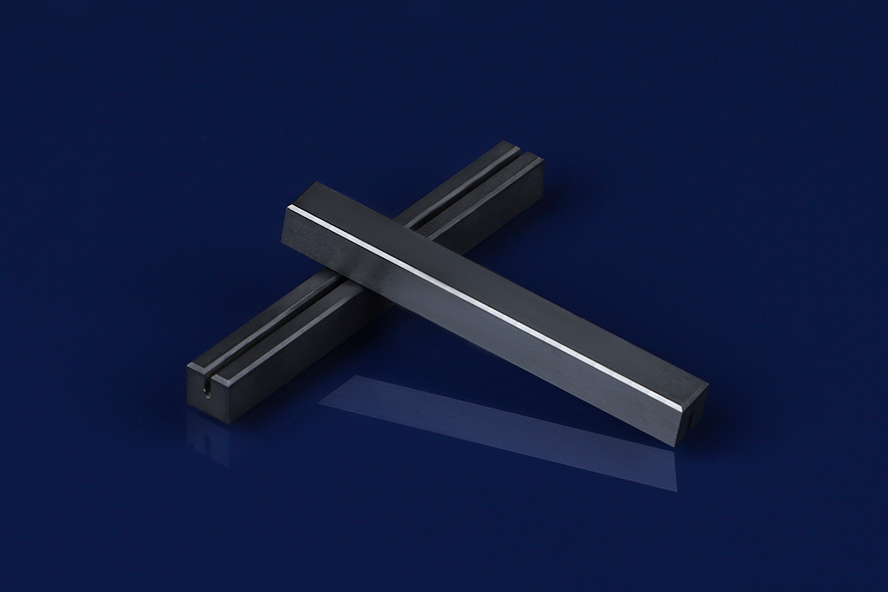


Silicon Carbide Ceramic Guide Rail
Silicon Carbide -


Reaction Bonded Silicon Carbide
Silicon Carbide
Silicon Carbide Material Properties
Properties of silicon carbide | Silicon carbide ceramics | ||
item | unit | Typical value | |
Physical property | |||
colour | black. | ||
density | g/cm³ | 3.1 | |
Gas permeability | 1300 | ||
hydroscopicity | 0.10% | ||
Mechanical property | |||
Monger hardness | Lv. | 9 | |
Rockwell hardness | HRA | 90 | |
Vickers Hardness (Hv50) | Gpa(kg/mm) | 500 | |
Bending strength (20 °C) | Mpa | 350 | |
Compressive strength (20 °C) | Mpa | 200 | |
Modulus of elasticity | Gpa | 300 | |
Poisson's ratio (20 °C) | 0.15 | ||
Fracture toughness (20 °C) | MPa*1/2 | 3 | |
Thermal performance | |||
Thermal conductivity (20 °C)-400°C | W/(m·K) | 150 | |
Thermal expansion | 10-6/℃ | 3×10^-6 /°C | |
Maximum service temperature | °C | 1600 | |
Electronic property | |||
Dielectric medium | KV/mm | 5 | |
Dielectric constant | Er | 4 | |
Dielectric loss Angle (1MHz) | 0.001 | ||
Silicon Carbide Machining
Silicon carbide (SiC) is classified as a difficult to machine material due to its high hardness and brittleness, and conventional cutting, drilling, and milling processes are difficult to effectively treat it. In order to achieve precision machining of silicon carbide ceramics, specialized tools and techniques are usually used.
Jundro is a globally leading silicon carbide company with extensive experience in machining SiC. Through our customized processing services, it has become an ideal choice for various high-precision equipment. We provide high-quality and precise ceramic components for various industries such as semiconductor, machinery, chemical, aerospace, etc. If you would like to inquire about customized machining parts, please contact us and our experts will be happy to assist you.



